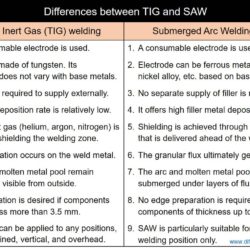
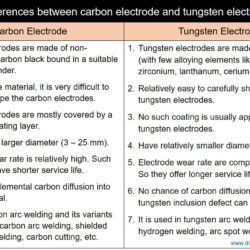
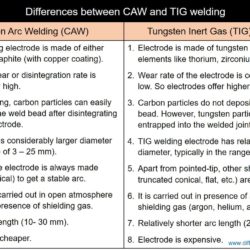
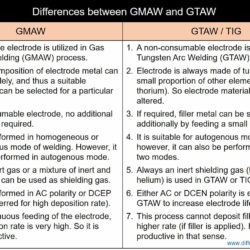
Difference Between TIG and SAW – Tungsten Inert Gas welding and Submerged Arc Welding
Arc welding is a subset of fusion welding process where the heat is supplied from an electric arc for melting the faying surfaces of the base metals for coalescence formation. This arc is established between an electrode and the base metals under sufficient potential difference. This arc welding electrode can be of two types – consumable and non-consumable. A consumable electrode is allowed to melt due to arc heat, and