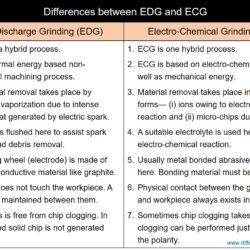
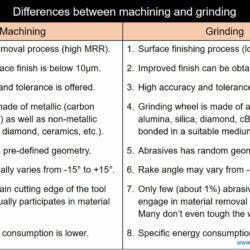
Difference Between EDG and ECG – Electro Discharge Grinding and Electro Chemical Grinding
Electric Discharge Grinding (EDG) is one thermal energy based non-traditional machining process that has apparent similarity in construction with the conventional grinding process. In EDG, a disc type metallic wheel is rotated about a fixed axis maintaining a small gap with the workpiece. The conductive wheel is given negative polarity, while the conductive workpiece is given positive polarity. The gap between wheel and workpiece is immersed with a suitable dielectric