Difference Between LBM and PAM – Laser Beam Machining and Plasma Arc Machining
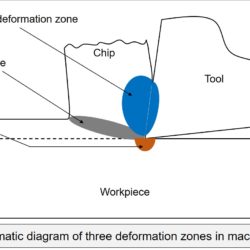
Non-traditional machining (NTM) processes can directly employ various forms of energy for removing material from workpiece in order to fabricate the intended 3-D feature. EDM, LBM, EBM, and PAM are four common NTM processes that use thermal energy (heat) to selectively remove material. In these processes, material removal mostly takes place in vaporized and sometimes in molten state. The source of heat is, however, different for these four processes. Laser