Difference Between PAM and IBM – Plasma Arc Machining and Ion Beam Machining
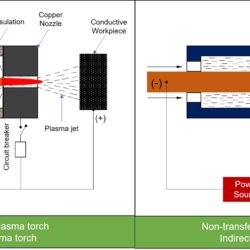
Different forms of energy (such as mechanical, thermal, electrical, chemical, electro-chemical, light, etc.) are directly utilized in advanced machining processes to realize material removal from the workpiece for fabricating intended 3-D feature following the subtractive manufacturing approach. Plasma Arc Machining (PAM) is one such advanced machining process where thermal energy (heat) is primarily used to melt down and vaporize material from the workpiece. A high temperature jet of thermal plasma