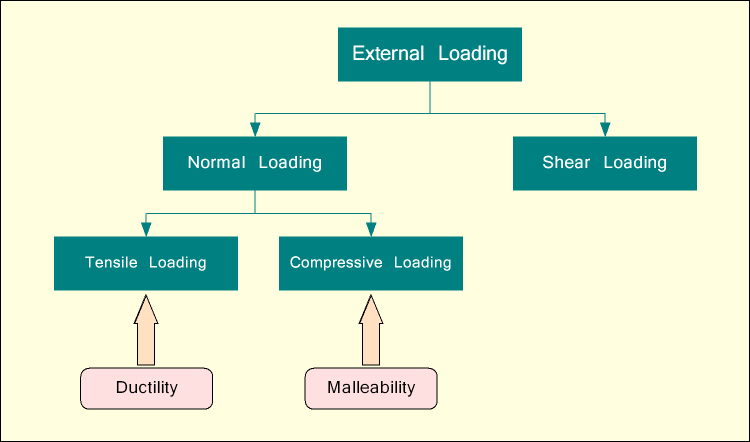
External load on a material can be applied in two different ways – normal loading and shear loading. Normal loading can again be classified into two categories, namely tensile loading and compressive loading. All other types of loading such as torsion, bending, etc. are just combination of these basic loading types. Now, when a material is subjected to substantial external load, it undergoes deformation. Initially, up to a very small extent, the deformation remains recoverable and then permanent deformation starts, which continues until fracture. The recoverable deformation is called elastic deformation, while the permanent one is termed as plastic deformation.
Plastic deformation under tensile loading is characterized by a property called ductility; while the same when occur under compressive loading is called malleability. By definition, ductility is the measure of the ability of a material to deform plastically under external tensile loading. This property is useful when material is undergoing tensile loading such as in wire drawing. Alternatively malleability is the measure of the ability of a material to deform plastically under external compressive loading. It is useful when material undergoes compressive loading such as in hammering, rolling, forging, etc. Similarities and differences between ductility and brittleness are explained in the following sections.
Similarities between ductility and malleability
- Both ductility and malleability are measures of the ability of a material to under plastic deformation.
- Both properties are affected by temperature and inbuilt stress within the material.
Differences between ductility and malleability
| Ductility | Malleability |
|---|---|
| Ductility is defined as the ability of solid material to plastically deform to a larger extent before crack appears when it is subjected to external tensile loading. | Malleability is defined as the ability of solid material to plastically deform to a larger extent before crack appears when it is subjected to external compressive loading. |
| Ductility of solid material decreases with increase in temperature. | Malleability of solid material increases with increase in temperature. |
| Materials that exhibit high ductility usually show high malleability. For example, gold and silver—both show excellent ductility and malleability. | Materials that exhibit high malleability may not show good ductility. For example, lead shows high malleability but poor ductility. |
| Ductility is crucial property when the solid is undergoing wire drawing operation because tensile force acts on it. | Malleability is crucial property when the solid is undergoing rolling, forging, extrusion, etc. operations because compressive force acts on it. |
References
- Book: Mechanical Behavior and Testing of Materials by A. K. Bhargava and C. P. Sharma (PHI Learning Private Limited). Buy this book
- Book: Introduction to Machine Design by V. B. Bhandari (McGraw Hill Education India Private Limited). Buy this book