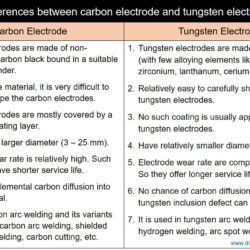
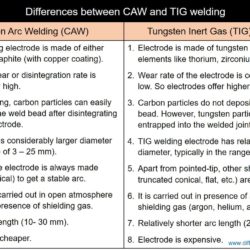
Difference Between Carbon Electrode and Tungsten Electrode for Arc Welding
Arc welding is one class of fusion welding where the faying surfaces of the base metals are melted by supplying heat through an electric arc. The arc is constituted between an electrode and the base metals. Arc welding electrodes can be broadly classified as consumable and non-consumable. While few arc welding processes utilize consumable electrode, others employ non-consumable electrode. Consumable electrodes are meant for melting during the welding to supply