Rake angle of the cutting tool is defined as the angle of orientation of tool’s rake surface from the reference plane (πR) and measured on some other plane. Depending on the plane on which it is projected and measured, it may have various names. At the same time, rake angle may have positive, negative or even zero value based on the inclination of rake surface from reference plane. Each of these three types has specific advantages and disadvantages. This value can influence cutting force and power consumption in machining, life of the cutting tool, chip deviation, shear angle, tool life, etc. Rake angle also indirectly affects machinability.
A positive rake reduces the wedge angle and thus shearing occurs smoothly with minimum shear deformation. Accordingly, cutting force and chip thickness ratio reduces. Also requirement of cutting power reduces, and thus larger values of process parameters can be employed to enhance material removal rate (or productivity). On the other hand, a negative rake offers a thicker tool tip, which increases both force resistant capability and life of the tool. So it is preferred while machining harder materials or machining with high chip load. However, negative rake leads to higher shear deformation of the chip, and thus cutting power requirement increases considerably. Important similarities and differences between positive and negative rake angles are discussed below. Following diagram schematically shows the positive and negative rake with projection on orthogonal plane.
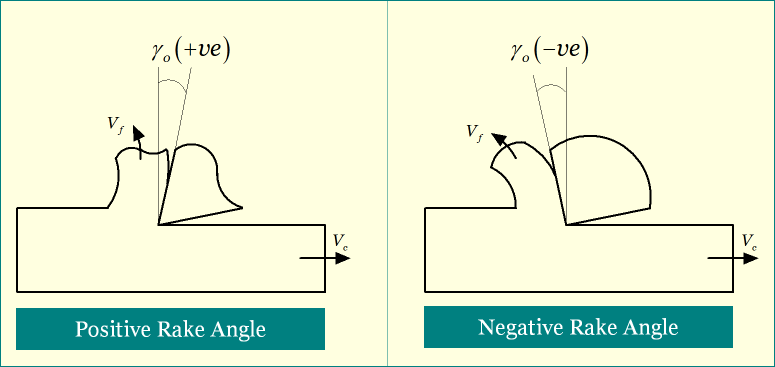
Similarities between positive rake angle and negative rake angle
- Both positive and negative rake angles indicate angular distance of cutting tool’s rake surface from reference plane; however, in opposite directions.
- None of them influences clearance angle or cutting angles of the cutter.
- Positive or negative rake does not usually rely on machining process, rather it depends on workpiece-tool material combination, feature type and intended machinability.
- Both positive and negative rake may present in a particular cutting tool, but in different directions. For example, a single point turning tool may have positive orthogonal rake angle and negative side rake angle.
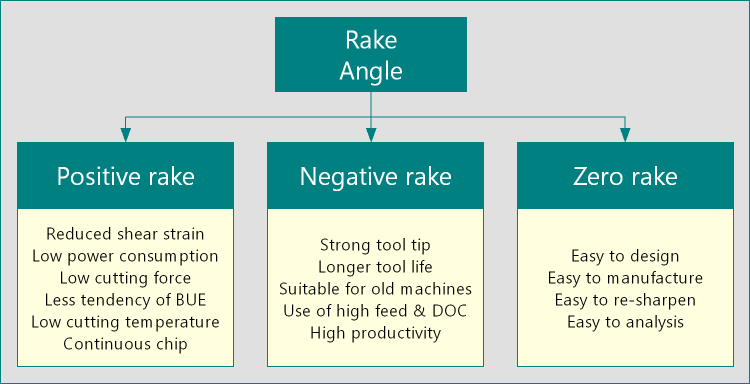
Differences between positive rake angle and negative rake angle
| Positive Rake Angle | Negative Rake Angle |
|---|---|
| Cutting tool with positive rake offers a sharp cutting edge. | Cutting tool with negative rake has less sharpness at the cutting edge. |
| Wedge angle of these tools is small. | For the same clearance angle, wedge angle of the tool is large. |
| Due to small wedge angle, tool tip has less strength and is prone to sudden breakage or catastrophic failure. | Large wedge angle provides a strong tool tip, which is more resilient to catastrophic failure. |
| Positive rake does not allow high chip load. So feed and depth of cut should be low. | Due to stronger tool tip, it allows higher chip load. This higher feed and depth of cut can be employed to increase MRR. |
| Positive rake results in less share deformation of chips during machining. | Negative rake results in large share deformation of the chips. |
| Positive rake tends to maintain the value of Chip Reduction Coefficient (CRC) lower. CRC is the ratio of chip thickness to uncut chip thickness and is inverse to the cutting ratio. | Negative rake tends to make the value of Chip Reduction Coefficient (CRC) higher. This indicates larger chip thickness for same uncut chip thickness. |
| Cutting force (and thus power) during machining with positive rake is quite small. | Cutting force (and thus power) during machining with negative rake is quite large for unchanged conditions and materials. |
| It helps in achieving continuous chip. | It usually provided discontinuous chips. |
| Usually, machinability is better with positive rake. | Usually, machinability is bad with negative rake. |
| Tool with positive rake is good for machining soft and ductile materials, such as copper, aluminum. | Tool with negative rake is good for machining hard and brittle materials, such as titanium, stainless steel. |
References
- Machining and Machine Tools by A. B. Chattopadhyay (Wiley).
- Metal Cutting: Theory And Practice by A. Bhattacharya (New Central Book Agency).